6.6 KiB
ants

A goroutine pool for Go
Package ants implements a fixed goroutine pool for managing and recycling a massive number of goroutines, allowing developers to limit the number of goroutines that created by your concurrent programs.
Features:
- Automatically managing and recycling a massive number of goroutines.
- Periodically clearing overdue goroutines.
- Friendly interfaces: submitting tasks, getting the number of running goroutines, readjusting capacity of pool dynamically, closing pool.
- Efficient in memory usage and it even achieves higher performance than unlimited goroutines in golang.
How to install
go get -u github.com/panjf2000/ants
Or, using glide:
glide get github.com/panjf2000/ants
How to use
If your program will generate a massive number of goroutines and you don't want them to consume a vast amount of memory, with ants, all you need to do is to import ants package and submit all your tasks to the default limited pool created when ants was imported:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
"time"
"github.com/panjf2000/ants"
)
var sum int32
func myFunc(i interface{}) {
n := i.(int32)
atomic.AddInt32(&sum, n)
fmt.Printf("run with %d\n", n)
}
func demoFunc() {
time.Sleep(10 * time.Millisecond)
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
}
func main() {
defer ants.Release()
runTimes := 1000
// Uses the common pool
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < runTimes; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
ants.Submit(func() {
demoFunc()
wg.Done()
})
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Printf("running goroutines: %d\n", ants.Running())
fmt.Printf("finish all tasks.\n")
// Uses the pool with a function,
// sets 10 to the size of goroutine pool and 1 second for expired duration
p, _ := ants.NewPoolWithFunc(10, func(i interface{}) {
myFunc(i)
wg.Done()
})
defer p.Release()
// Submits tasks
for i := 0; i < runTimes; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
p.Serve(int32(i))
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Printf("running goroutines: %d\n", p.Running())
fmt.Printf("finish all tasks, result is %d\n", sum)
}
Integrate with http server
package main
import (
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"github.com/panjf2000/ants"
)
type Request struct {
Param []byte
Result chan []byte
}
func main() {
pool, _ := ants.NewPoolWithFunc(100, func(payload interface{}) {
request, ok := payload.(*Request)
if !ok {
return
}
reverseParam := func(s []byte) []byte {
for i, j := 0, len(s)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 {
s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i]
}
return s
}(request.Param)
request.Result <- reverseParam
})
defer pool.Release()
http.HandleFunc("/reverse", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
param, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "request error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
defer r.Body.Close()
request := &Request{Param: param, Result: make(chan []byte)}
// Throttles the requests with ants pool. This process is asynchronous and
// you can receive a result from the channel defined outside.
if err := pool.Serve(request); err != nil {
http.Error(w, "throttle limit error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
w.Write(<-request.Result)
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
Submit tasks
Tasks can be submitted by calling ants.Submit(func())
ants.Submit(func(){})
Custom limited pool
Ants also supports custom limited pool. You can use the NewPool method to create a pool with the given capacity, as following:
// Sets 10000 the size of goroutine pool
p, _ := ants.NewPool(10000)
// Submits a task
p.Submit(func(){})
Tuning pool capacity
You can change ants pool capacity at any time with ReSize(int):
pool.ReSize(1000) // Tunes its capacity to 1000
pool.ReSize(100000) // Tunes its capacity to 100000
Don't worry about the synchronous problems in this case, this method is thread-safe.
About sequence
All the tasks submitted to ants pool will not be guaranteed to be processed in order, because those tasks distribute among a series of concurrent workers, thus those tasks are processed concurrently.
Benchmarks
OS : macOS High Sierra
Processor : 2.7 GHz Intel Core i5
Memory : 8 GB 1867 MHz DDR3
Go1.9
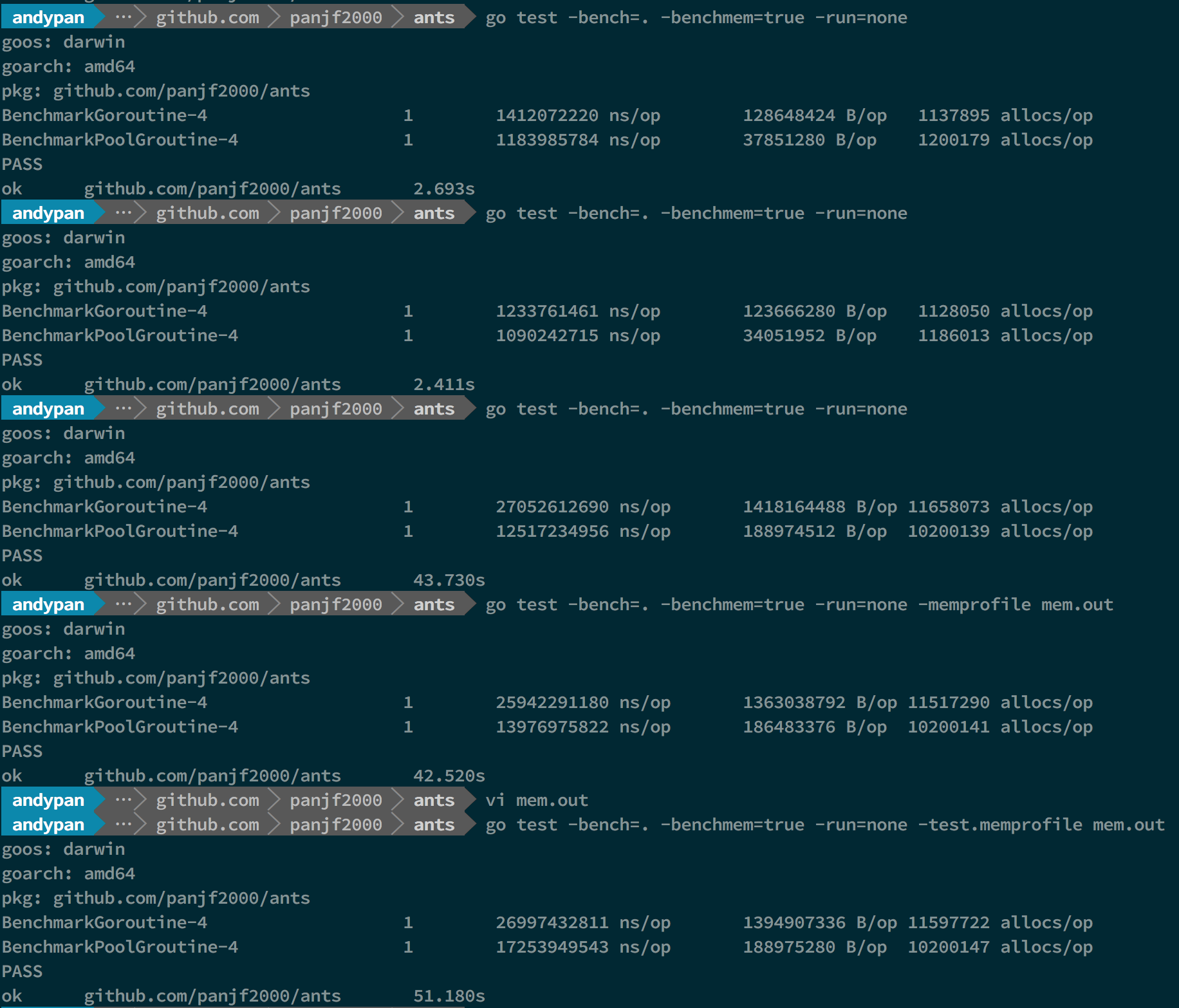
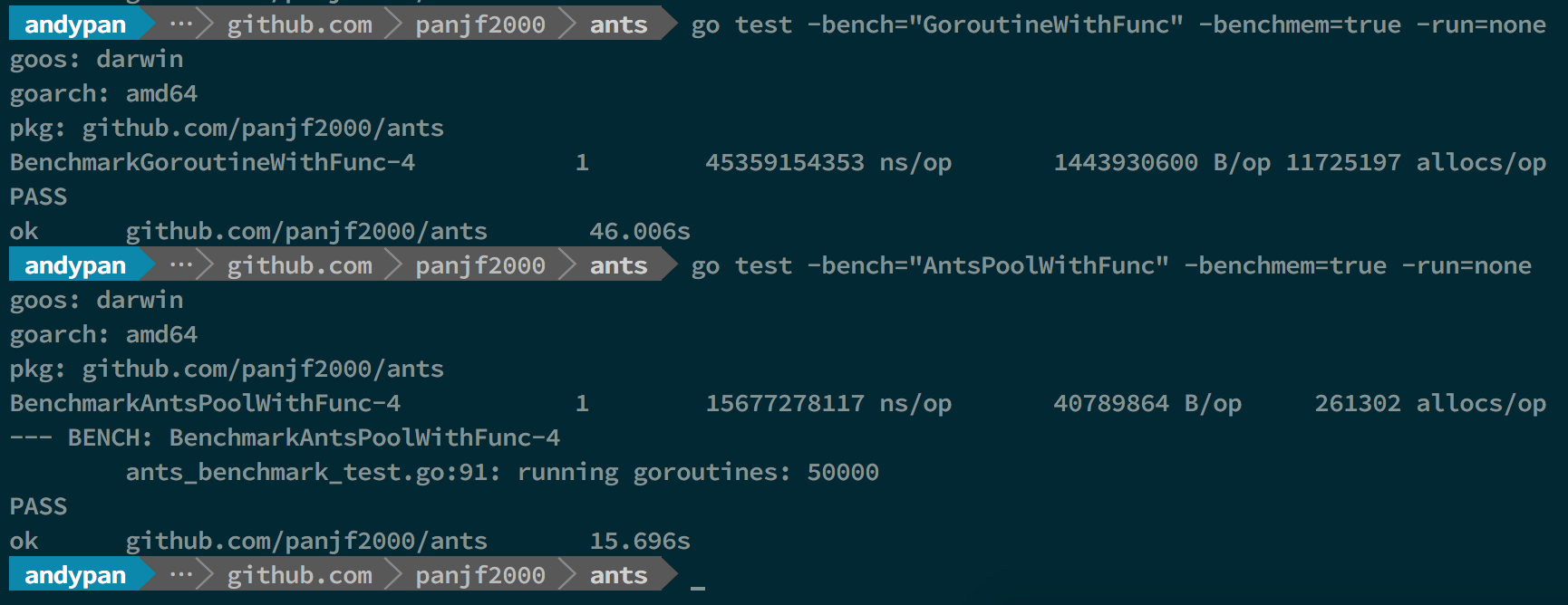
In that benchmark-picture, the first and second benchmarks performed test with 1M tasks and the rest of benchmarks performed test with 10M tasks, both unlimited goroutines and ants pool, and the capacity of this ants goroutine-pool was limited to 50K.
-
BenchmarkGoroutine-4 represents the benchmarks with unlimited goroutines in golang.
-
BenchmarkPoolGroutine-4 represents the benchmarks with a ants pool.
The test data above is a basic benchmark and the more detailed benchmarks will be uploaded later.
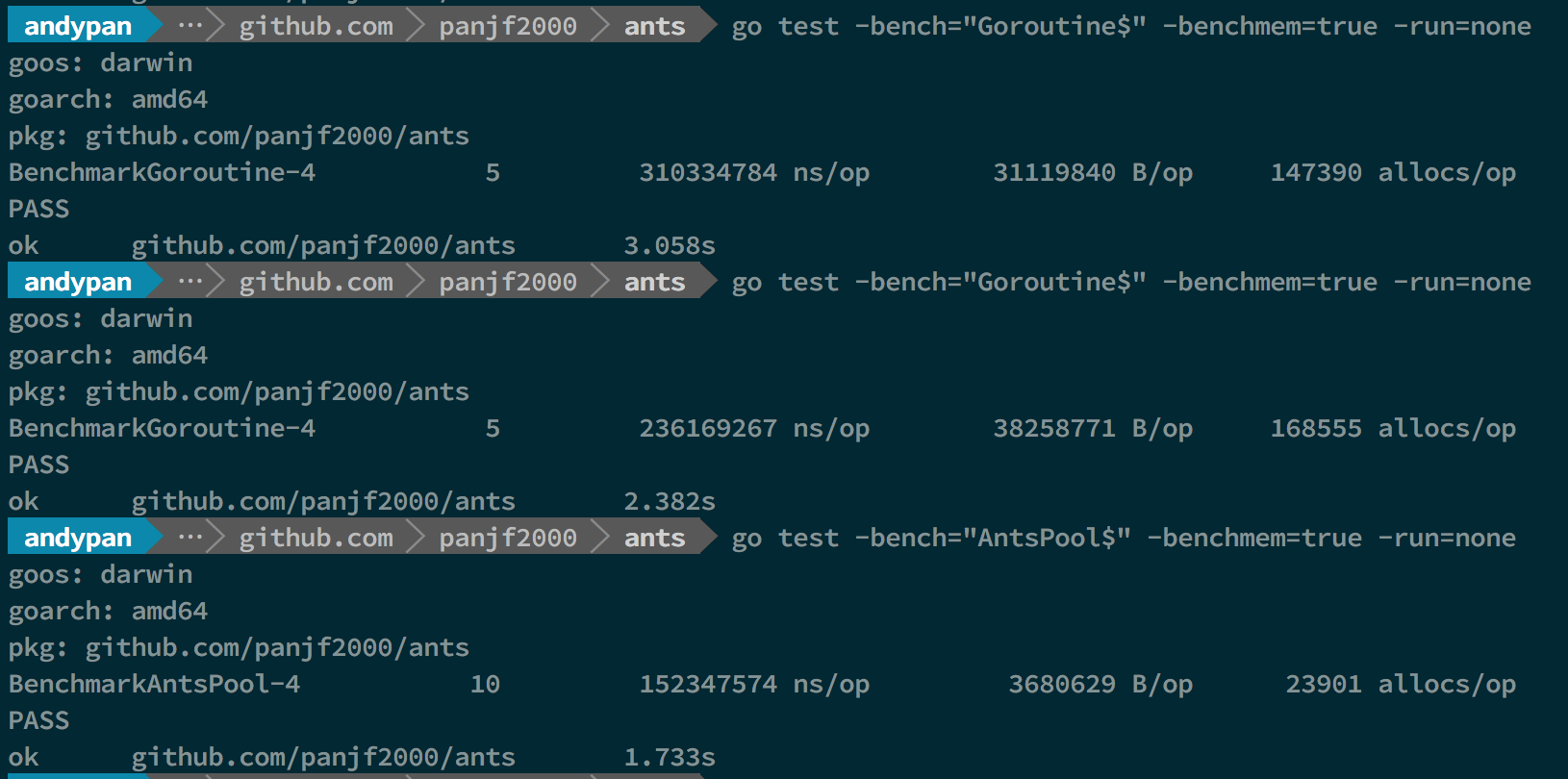
Benchmarks with Pool
In that benchmark-picture, the first and second benchmarks performed test with 1M tasks and the rest of benchmarks performed test with 10M tasks, both unlimited goroutines and ants pool, and the capacity of this ants goroutine-pool was limited to 50K.
As you can see, ants can up to 2x faster than goroutines without pool (10M tasks) and it only consumes half memory comparing with goroutines without pool. (both 1M and 10M tasks)
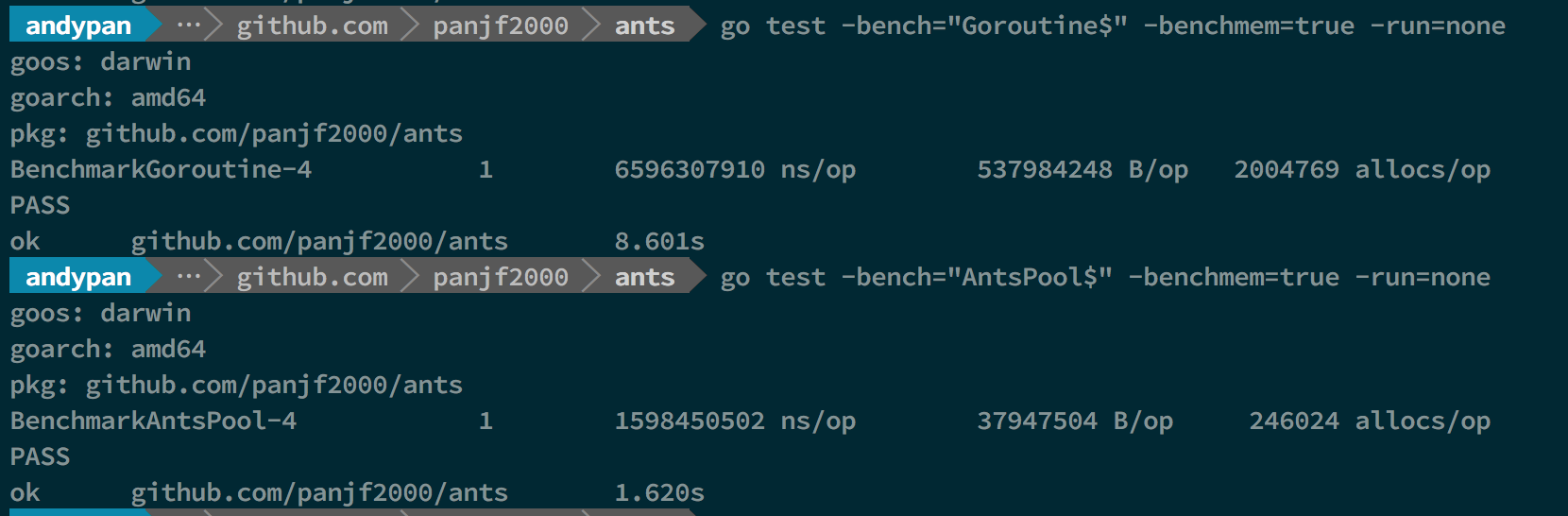
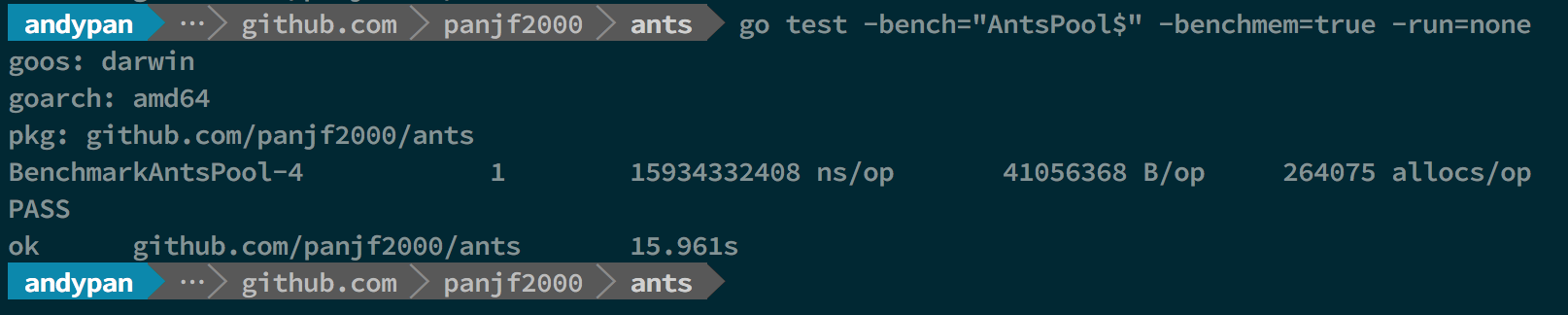
Benchmarks with PoolWithFunc
Throughput (it is suitable for scenarios where asynchronous tasks are submitted without concern for results)
100K tasks
1M tasks
10M tasks
There was only the test of ants Pool because my computer was crash when it reached 10M goroutines without pool.
As you can see, ants can up to 2x~6x faster than goroutines without pool and the memory consumption is reduced by 10 to 20 times.